- Institute : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/institute/
- Zusammenarbeit : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/zusammenarbeit/
- Internationale Projekte : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/internationale-projekte/
- Agenda : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/agenda/
- News : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/news/
- Kontakt und Anreise : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/kontakt-und-anreise/
- TechTransfer : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/techtransfer/
- Institute : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/institute/
- Zusammenarbeit : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/zusammenarbeit/
- Internationale Projekte : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/internationale-projekte/
- Agenda : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/agenda/
- News : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/news/
- Kontakt und Anreise : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/kontakt-und-anreise/
- TechTransfer : /de/anwendungsorientierte-forschung/techtransfer/
International Projects
The participation of the HEIA-FR in international research and innovation projects is extremely important for the development of its network, for its openness to other sensibilities and for the promotion of its know-how.
European Union Research Framework Programmes
PEARL-DNA
In a world driven by data, the need for innovative and sustainable data storage solutions has never been more pressing. PEARL-DNA is set to revolutionise the way we handle data storage, reshaping the future of DNA-based data storage.
Data fuels the pulse of modern society - driving advancements in artificial intelligence, healthcare, astronomy, climate science, and countless other fields. The need to store massive data sets efficiently and sustainably has become a top priority for researchers and industries worldwide. Simultaneously, more than 6 billion smartphone users are generating constant streams of location data, photos and videos with data storage demand. The challenge: The world is running out of data storage. At the same time, current technologies for digital data storage have hit various technological and sustainability limits. A significant share of new data is not yet stored beyond the short term, and conventional storage media do not have the capacity, longevity, or data density to meet global demand.
Under the Horizon-EIC-2022-PATHFINDERCHALLENGES-01-05 call, PEARLDNA emerged as one of the eight selected proposals, securing 5.04 million Euros in funding. Successfully kicked-off on October 1, 2023, this ambitious project aims to develop and evaluate a complete end-to-end chain of innovative next generation solutions for DNA-based digital data storage, offering an environmentally sustainable solution to the data challenges of today and tomorrow. The overall goal of the PEARL-DNA project is to deliver a proof of concept (PoC, TRL4) for its end-to-end platform’s systems and processes. With a focus on surpassing existing technologies in data recording throughput, speed, capacity, reliability, and data integrity, PEARL-DNA harnesses DNA’s inherently superior data density and longevity to establish DNA-based digital data storage as the ultimate archival storage medium for a sustainable future. The platform will be developed in a fully modular and interoperable way, promoting seamless integration with other DNA-data storage solutions to accelerate the uptake and wide adoption of the PEARL-DNA technology.

Responsible for the project
Start Date
October 2023
End Date
September 2026
Funding Type
Horizon Europe EIC Pathfinder
More information
H2020 - ORCHESTRA
Orchestra aims to orchestrate traffic management across all transport modes and in the presence of connected and automated vehicles.
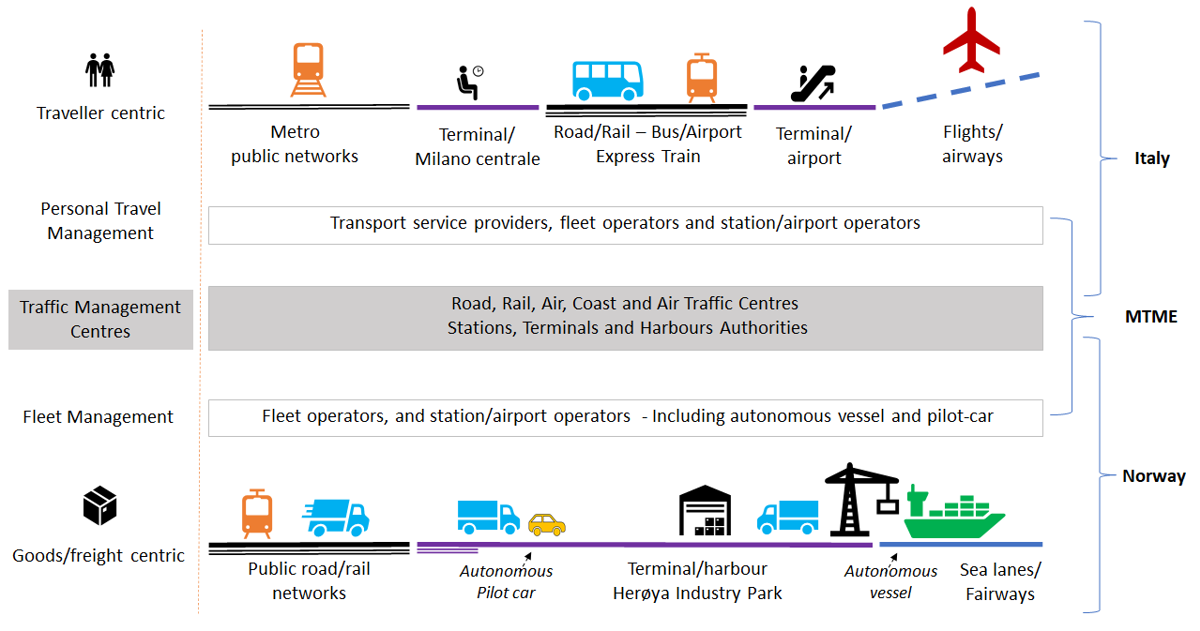
The ambition is to design a multimodal traffic management ecosystem and build and demonstrate technical solutions, organisational aspects, processes, and tools. In addition, simulations will train personnel to work with the new solutions in various scenarios.
Traffic management traditionally coordinates traffic flows within “their silo” (road network, railway network, a set of fairways, air corridors, etc.). The introduction of Connected Autonomous Vehicles, and new situations, as exemplified by the COVID-19 pandemic, stresses the conventional transport systems and questions if they are robust and resilient enough. In ORCHESTRA, a multimodal traffic management ecosystem will be designed to handle changes in requirements and procedures efficiently and assess whether laws, regulations, management, and organisational practices are designed for optimal handling of both normal operations and crises.
The long-term vision of ORCHESTRA is a future where it is easy to coordinate and synchronise traffic management of all modes (road, sea, air and rail), to cope with diverse demands and situations. ORCHESTRA will facilitate optimal transport networks and efficient multimodal transport services, both in rural and urban areas, for people and goods. ORCHESTRA will bridge the current silos within traffic management.
Traffic management for sea, road, rail and air transport should work together to support new multimodal transport services. It needs to facilitate better utilisation and more resilience in all situations – from daily operations to disasters.
ORCHESTRA will support key stakeholders, including practitioners, policymakers, public authorities, transport providers, and users, with tools and best practices to enhance collaboration and synchronising multimodal traffic management. The project will assess rules and regulations for data governance and sharing and efficient traffic management, supported by intelligent infrastructure and CAVs.
The project's solutions will be prototyped and evaluated in two Living Labs. This will provide concrete evidence on how technological capabilities and organisational practices can be integrated to optimise transport through selected use cases. Demonstrations include coordinating freight and passenger flows across modes in a dynamic, safe, secure, and sustainable manner. The use cases will be upscaled through simulations to evaluate complex multi-actor actor scenarios and manage irregularities (including disasters).
- Milan Malpensa airport will focus on efficient door-to-gate routing according to preferences (fastest, cheapest, etc.) to optimising traffic and passenger flow in Italy.
- In Norway Herøya Industrial Park, the pilot will focus on fully automatization by facilitating and aligning traffic management measures.
ROSAS, one of the Centre of Competence of the HEIA-FR is playing an important role in the Orchestra project as it is leading one of the major work packages: "Living Labs, trials and simulation".

Responsible for the project
Vincent Robatel
Start Date
1st of May 2021
End Date
29 of February 2024
Funding Type
H2020
More information
H2020 – MarketPlace
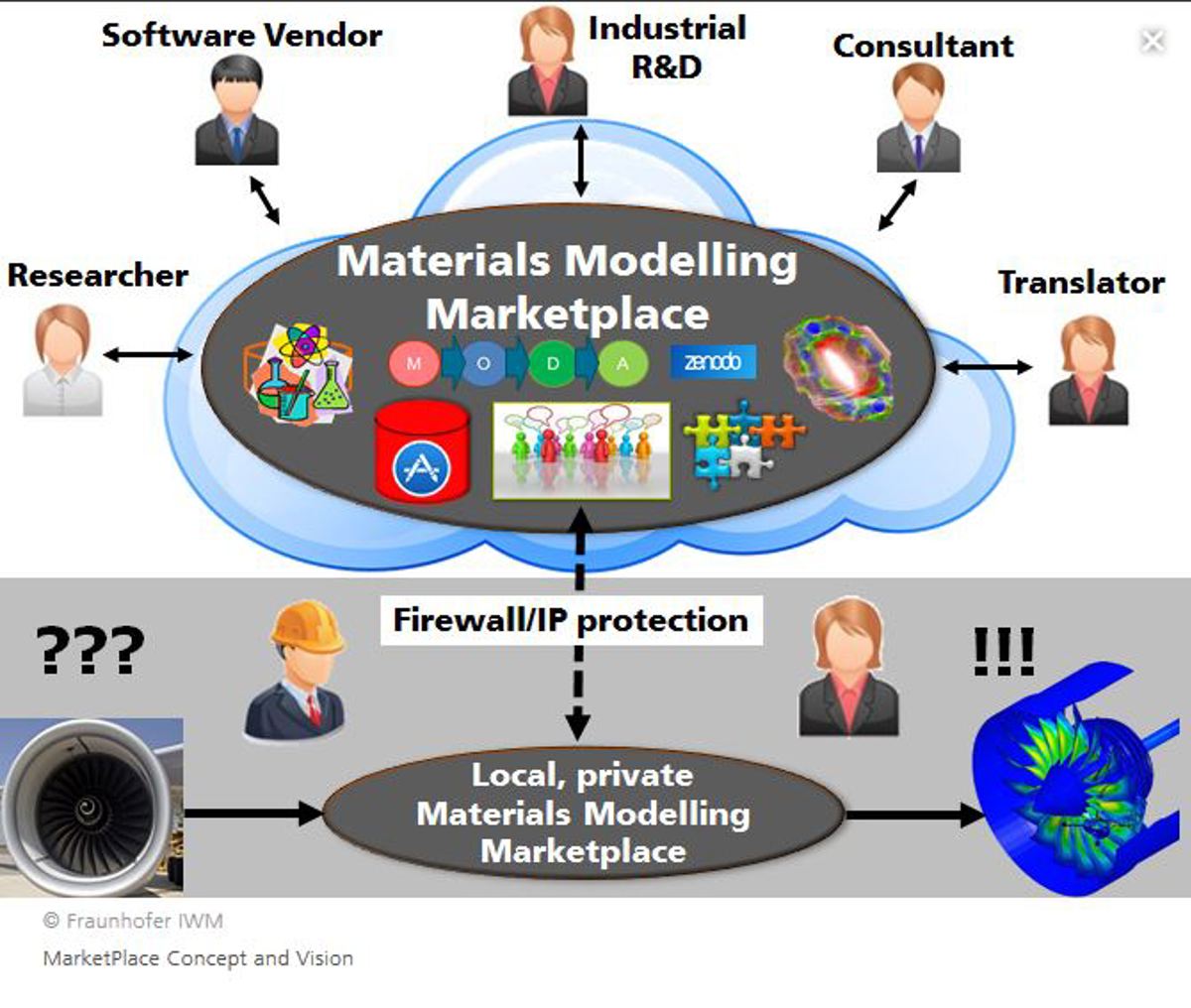
Provide seamless and rapid access to all relevant elements required for novel deployment of materials modelling in the industry
The concept of the MarketPlace is to leverage recent software engineering and ICT advances to collect, adapt and integrate all scattered modelling components from all fragmented materials modelling and industrial communities and provide a single point of access - an online gateway - to all materials modelling activities in Europe.
MarketPlace aims not only at information components but also provides the mechanisms and services to create and apply advanced materials modelling workflows. All this is directly made possible on the MarketPlace integrated web platform and through connectivity to externally linked High-Performance-Computing (HPC) resources (e.g., PRACE) and database warehouses (e.g., Zenodo).
Responsable du projet
Rudolf Koopmans
Date de début
Août 2018
Date de fin
Décembre 2022
Type de financement
H2020
H2020 - BioSmart
Bio-based smart packaging for enhanced preservation of food quality
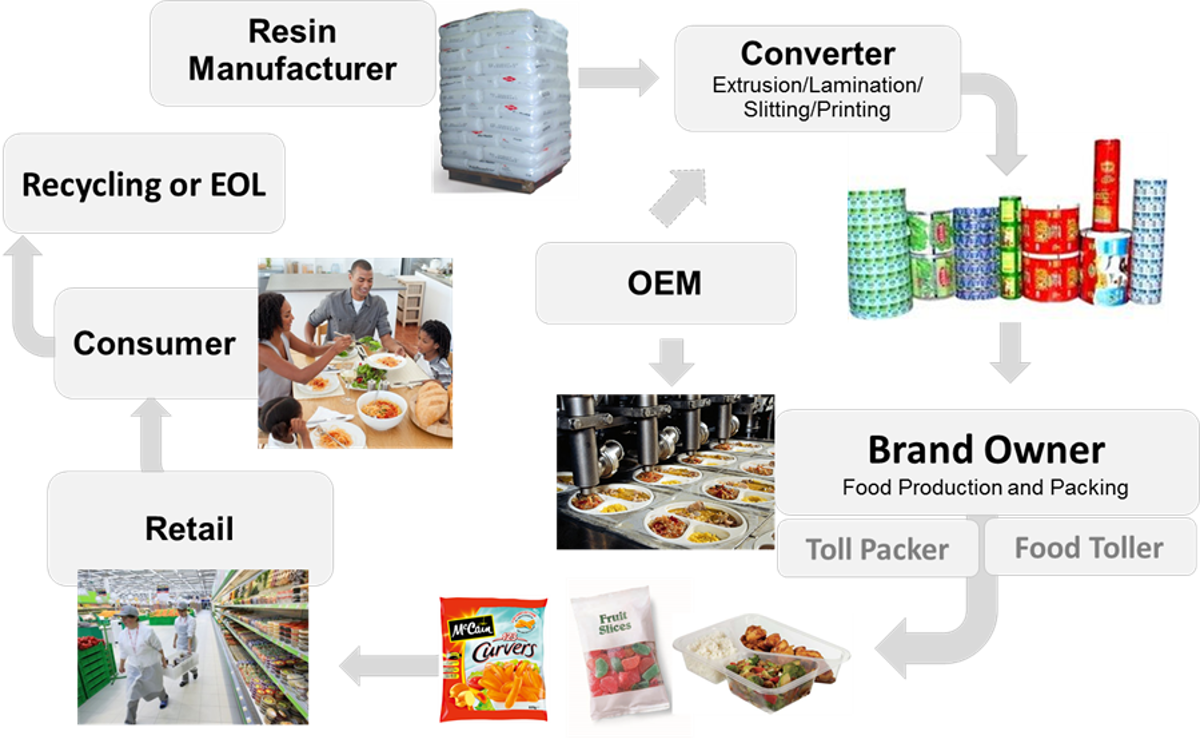
A holistic ecosystem approach is pursued by offering solutions that bring enhanced performance and acceptable economics to the value chain and facilitate implementation and large-scale commercialization. Critical issues that differentiate the present packages from the future all-bio-based and compostable ones are enhanced active and smart functionalities that make possible: light weighting, reduced food residues, shelf life monitoring and longer shelf life, easier consumer waste handling, and all this at a competitive cost to the incumbent.
The BIOSMART project develops thus encompasses an approach for selectively integrating super-hydrophobic surfaces, microencapsulated phase change materials, barrier coatings, sensoring devices, and new bio-active antimicrobial and antioxidants, into all-bio-based multilayer flexible plastic packages. Three generic packaging systems are selected with specific performance needs as defined by current multi-material (e.g. pouches, terrines and cardboard/thin film tray). The associate life cycle assessments for the different possible scenarios include economic feasibility. Ultimately, this consolidated knowledge is captured in a material selection and packaging performance simulation App. through optimization of all possible variables to meet selected key performance indicators (KPI). The BIOSMART project will develop active and smart bio-based and compostable packages to meet the needs of both fresh and pre-treated food applications. In addition, the novel packaging system will form the basis for tailoring performance and functionality to specific flexible and rigid food packages in diverse market segments.
In order to address future demands, packaging will need to enable lightweighting, reduced food residues, easier shelf life monitoring and longer shelf life, easier consumer waste handling, all without a price premium. The BIOSMART project, therefore, encompasses an approach for selectively integrating superhydrophobic surfaces, microencapsulated phase change materials, barrier coatings, sensor devices and new bio-active antimicrobial and antioxidants, into fully bio-based multilayer flexible plastic packages. Current food packages typically are lightweight and address highly tailored performance needs. However, they are composed of multiple and different plastics often including aluminium. These are difficult to recycle for individual components, do not address residual food issues or guarantee the real food due-date. The challenge is addressed by developing an all compostable strongly simplified package with modifiable mechanical and barrier properties, “non-sticky” surfaces and real due-date sensors. The novel package is “good enough” for most food applications, the entire package is “organic” for easy collection and composting.
Responsable du projet
Rudolf Koopmans
Date de début
Mai 2017
Date de fin
Avril 2021
Type de financement
H2020
H2020 - NESTORE
NESTORE is an innovative coach that aims to accompany people as they age by offering personalised advices and support decision-making so that we can maintain our wellbeing and extend the number of years we live independently
Due to longer life expectancy and declining fertility rates, Europe’s ageing population is growing fast. In order to maximize our wellbeing as we age and to reduce the economic burden on our welfare systems, we need to adopt preventive policies that will promote active and healthy ageing. These policies must commit to a life-course approach to ageing that will address the cumulative impact of people’s life experiences and discriminations.
Longer life expectancy does not necessarily come with more years of life in good health. Acknowledging the correlation between ageing demographics and the increasing number of people living with chronic diseases, the World Health Organisation recommends adopting a life-course preventive approach based on age-friendly environments the provision of community-based services answering older adults’ needs.
Faced with pressing health needs of the global ageing population, adequate adjustments of our social, economic and public health policies are of the utmost importance. The good news is: research and technological development can help our societies take up the challenge.
In this complex context, NESTORE proposes to support healthy older people to sustain their wellbeing and capacity to live independently by promoting customised pathway to wellbeing.Technically speaking, NESTORE’s ambitious objective is to develop an innovative, multi-dimensional, cross-disciplinary and personalized coaching system that, leveraging ICT social connectivity, will support older adults by encouraging them to become co-producers of their wellness.
Eventually, the project will develop a companion providing people with guidance for longer healthy life years.The NESTORE system will operate into the physical and virtual domains through tangible objects and sensors, as well as software and apps enabling monitoring and coaching.

Project Lead
Elena Mugellini
Start Date
November 2017
End Date
November 2020
Type of financing
H2020
Partners
16 partners from 8 European countries: Belgium, Italy, Netherlands, Romania, Spain. Switzerland and the United Kingdom
Interreg: Cross-border Cooperation in Europe
Interreg A - Sylvo
Utilisation de biochars de bois pour le traitement des eaux usée et de réinfiltration de nappes phréatiques
Dans un proche avenir, développements agricole, urbain et industriel seront fortement liés à la disponibilité d’une eau de qualité (et seront concurrents pour celle-ci). Les modèles de changement climatique prévoient une modification temporelle des flux d'eau venant des réservoirs alpins avec des pics en sortie d'hivers et en fin d'été, ne correspondant pas aux pics de besoins (urbains, énergétiques, agricoles). Il va falloir donc pour des villes de grande taille avoir recours, plus encore qu'aujourd'hui, à un stockage de l'eau dans des réservoirs souterrains (aquifères rechargés artificiellement). La qualité des eaux ainsi stockée est affectée tant par les pollutions géogéniques (relarguées par le milieux souterrain) que par les eaux utilisées pour leur recharge, contaminées de façon croissante en micropolluants (résidus médicamenteux, de soins corporels ou de produits d’’entretien de surfaces). La protection de ces écosystèmes naturels devient donc un enjeu majeur.
La pollution de l'aquifère de l'Arve par des résidus médicamenteux a été mise en évidence dans un récent projet INTERREG franco-suisse IRMISE (2013-2015). Cette pollution diffuse a comme source, l'agriculture et les traitements médicaux, directement ou via les eaux usées après traitement, car les stations d'épuration actuelles (STEP) ne sont pas équipées pour éliminer ce type de pollution. Ces eaux étant destinées à la boisson, il en résulte un besoin de traitement, soit dans les stations d'épuration, soit dans les stations de pompage. Cette thématique a déjà trouvé écho auprès du législateur suisse qui a inscrit dans la loi l'obligation de traitement des micropolluants dans les STEP de grande taille, jusqu'à obtenir une performance de 80% d’élimination (LEaux, RS 814.20). Deux voies de traitement sont privilégiées, le traitement par charbons actifs, ou le traitement par ozonation. Dans le premier cas, les charbons sont importés, et représentent un mélange de diverses sources, dont des charbons fossiles, souvent riches en métaux lourds.
La nouvelle demande en épuration des eaux par des charbons actifs aboutit à un marché en pleine expansion. Seulement pour le secteur du traitement des eaux usées, les volumes à épurer permettraient dans une première estimation grossière de générer une activité économique de plusieurs dizaines de millions de francs par année si l'on se réfère uniquement aux besoins du territoire Suisse.
Face à ce constat, la recherche d'une meilleure solution semble doublement pertinente.
L'économie du bois est un secteur d'activité important en Suisse et dans la région frontalière des pays de Savoie. Les différents produits et sous-produits du bois trouvent une place sur le marché économique, en particulier dans les filières énergétiques. Cependant, parmi ces sous-produits, certains ne trouvent pas de seconde vie ou pourraient trouver de meilleures voies de valorisation. Par exemple, après transformation sous forme de biochar suite à une pyrolyse (combustion en absence d'oxygène), les déchets à faibles pouvoir calorifique pourraient venir alimenter le marché de la demande en charbons actifs pour l'épuration des eaux usées et des eaux de surface ou pour la potabilisation des eaux de boisson, en remplacement des charbons d'importation.
Les unités de transformation des biomasses en biochar existent soit à l'échelle industrielle, soit à des échelles de petites entreprises, fixes ou mobiles. Ceci permet donc une grande adaptation aux tailles des entreprises des filières bois, allant du simple propriétaire forestier, aux grandes scieries en passant par les grands domaines forestiers publics.
Le projet Sylvo a pour objectif de répondre aux questions suivantes :
- Quelles sont les performances de traitement que l’on peut obtenir de biochars produits à partir de biomasses provenant de l’industrie forestière et du bois ?
- Quelles sont les caractéristiques processus/produit à développer pour obtenir une performance d’épuration optimisée?
Quelle est la viabilité économique et écologique de cette filière (les aspects écologiques constituant un argument de vente important) ?

Project Lead
Fabienne Favre Boivin
Start Date
January 2017
End Date
August 2021
Type of Financing
Interreg France Switzerland
Interreg A - JURAD-BAT
Améliorer la gestion du risque radon dans les bâtiments de l’Arc jurassien : une plateforme transfrontalière au service des usagers et des professionnels concernés
Fruit de la collaboration fructueuse et de longue date de l’Office fédéral de la santé publique (OFSP) et de la Haute École d’ingénierie et d’architecture de Fribourg (HEIA-FR) avec la Démarche pluraliste radon de Franche Comté, ce projet vise le renforcement et la mise en commun de compétences professionnelles en matière de gestion du risque radon et qualité de l’air dans les bâtiments de l’Arc jurassien.
Il a pour objectif de développer une plateforme web transfrontalière pour favoriser la mise en commun de compétences, le partage d’expériences et la formation des professionnels de la construction, mais aussi des collectivités territoriales en matière de gestion du risque radon. Ce traitement du risque s’intègre plus globalement dans une démarche de santé publique au sein des bâtiments de l’Arc jurassien, en considérant la qualité générale de l’air intérieur et la problématique de l’efficacité énergétique.
Les compétences conjointes de la France et de la Suisse servent de socle à la création d’un outil d’aide à la décision à destination des élus, comme des particuliers et des professionnels du bâtiment. Il favorisera une meilleure gestion du risque sanitaire associé à la présence de radon dans les bâtiments, tout en assurant une bonne qualité de l’air intérieur.
Plus d’information : promotion de la plateforme Jurad-Bat et site internet.

Project Lead
Joëlle Goyette Pernot
Start Date
September 2016
End Date
June 2020
Type of Financing
Interreg A
Parters
Switzerland :
OFSP, ECONS SA, EHE SA, PLANAIR SA
France :
Université de Franche-Comté, ATMO-BFC, CEPN, CEREMA, IRSN, PMA, Pavillon des sciences
Interreg B - ARDIA-Net
ARDIA-Net aims to develop a multilevel, multinational and coherent Alpine RDI Area for cross-regional and interdisciplinary cooperation and implement a joint funding framework and pilot projects addressing circular bio-economy and health economy megatrends.
The recent experience gained in the Interreg-project S3-4AlpClusters shows that there is a persistent funding gap for cross-regional research, development and innovation (RDI) projects targeting S3 opportunities of particular relevance and including actors of new value chains, from research to market. S3 across the Alpine Space rely on existing capacities in relevant priority areas, such as digitization, agro-food, health and materials, which represent huge synergy potentials at cross-regional level. The ARDIA-Net challenge is to create a multilevel, multinational and coherent Alpine Space Research, Development and Innovation (RDI) Area, which addresses the regions’ specific capacities by synchronizing and funding joint activities across regions. ARDIA-Net will result in a ready-to-use funding environment and innovation beacons for future cooperation in S3-implementation.
The ARDIA-Net project is led by BIOPRO Baden-Württemberg (DE) and involves 7 other partners: Bavarian Research Alliance (DE), Business Upper Austria (AT), Innovation and Technology Transfer Salzburg (AT), Lombardy Green Chemistry Association (IT), Poly4EmI (SI), University of Applied Sciences and Arts Western Switzerland – School of Engineering and Architecture of Fribourg (CH) and SC Sviluppo Chimica (IT).

Project Lead
Jacques Bersier / Michael Keller
Duration
Start Date: 01/10/2019
End Date: 30/6/2022
Type of Financing
Federal Office for Spatial Development
Fribourg Development Agency
HEIA-FR
Funding (Euro)
Total eligible costs 1'541'414
ERDF Grant 1'169'952
Interreg B - AlpLinkBioEco
Linking BioBased Industry Value Chains Across the Alpine Region
The transition from a linear fossil-fuel based to a circular bio-based economy is a key EU objective. To achieve this objective, the Alpine Space (AS) regions have significant biomass resources, strong industry sectors, and knowledge centers. Unfortunately, no holistic cross-regional approach exists to connect all relevant actors. The huge potential remains untapped for lack of innovative bio-based value chains (VCs). Thus, the AS regions have a common challenge to bring together bio-feedstock producers, intermediates processors, product developers, brand owners, retailers and product end-users to address pressing societal needs with novel cross-regional and sectorial value chains for implementing a circular bio-based economy.
The project's main objective is precisely to develop a cross-regional circular bio-based economic strategy that includes a roadmap and demonstrators for intelligently assessing, selecting and creating innovative VCs for the AS wood, agriculture, food/pharma and chemistry sectors.
- Existing resources, actors and relevant policies are mapped to set up a cross-regional database.
- A methodology (VC generator) is developed to match actors demand-oriented in new or alternative VCs. It enables new cluster activities for novel business development and defining coherent data-driven policies for stimulating the AS circular bio-based economy.
- The project identifies previously untapped growth opportunities with demonstrators for each selected sector for the production of bio-based high added-value applications and products.
Furthermore, a Masterplan on the circular bio-based economy is delivered for establishing common framework conditions on innovation and data-driven policy dialogues within the AS. The project targets all relevant stakeholders including, policymakers, cluster initiatives, sectoral agencies, research centres, SMEs and individual actors, who can benefit from the specific tools and engagement in the novel VCs.

Project Lead
Jacques Bersier / Rudolf Koopmans / Michael Keller
Duration
Start Date: 14/04/2018
End Date: 16/04/2021
Type of Financing
Federal Office for Spatial Development
Fribourg Development Agency
HEIA-FR
Funding (Euro)
Total eligible costs 2'291'020
ERDF Grant 1'730'617
Interreg B - S3-4AlpClusters
Smart Specialisation Strategies to build an Innovation model for Alp Clusters
The Smart Specialisation concept is a lever of EU Cohesion Policy. Several EU regions developed Smart Specialization Strategies (S3). Challenge is to implement S3 through clusters to gain sustainable and incl. growth generating critical mass. No many experiences exist due to lack of knowledge about S3 in other regions. Implementation tools must be developed to fully benefit SMEs. The objective is to improve framework conditions for innovation induced by clusters and SMEs and to create new jobs.
S3 implemented by clusters is an innovative approach that improves innovation in the Alpine Space. The cross-regional approach supports coordinated actions between the different sectors/regions. Transnational cluster cooperation brings SMEs critical mass and enhances cross-regional collaboration to innovate for new products in the relevant areas of the Alpine Space.
Project outputs are: joint transnational cluster action plan and S3 stress test analysis of advanced, convergence and less advanced regions for agenda setting, strategy development and implementation ' outline for a synchronised scheme - S3-based innovation model adapted to regional clusters ' better framework conditions for companies through tested innovation model and services. Quadruple helix benefits from these outputs to boost innovation. The work is jointly completed by pilot clusters, entrepreneurs, academics, and supported by public authorities, clusters and S3 experts. Cluster policies will shift 'to concentrate resources on the development of those activities that are likely to transform the existing economic structures through R&D and innovation'. Transnational approach bundles the strengths of Alpine regions and SMEs towards smart innovation: they learn from each other through good and bad practices. S3 partners mutual knowledge facilitates framework conditions creation.

Project Lead
Jacques Bersier / Michael Keller
Duration
Start Date: 01/11/2016
End Date: 30/04/2019
Type of Financing
Federal Office for Spatial Development
Fribourg Development Agency
HEIA-FR
Funding (Euro)
Total eligible costs 2'521'964
ERDF Grant 1'929'500
Interreg B - THE4BEES
Changer le comportement des utilisateurs pour réduire la consommation d'énergie et des émissions de GES des bâtiments
THE4BEES se fonde sur le constat que les occupants d'un bâtiment influencent par leur comportement le bilan énergétique et les émissions de gaz à effet de serre (GES) induites par ce bâtiment.
La plupart des stratégies actuelles pour atteindre l'efficacité énergétique dans les bâtiments se concentrent sur des mesures techniques et sur les phases de conception et planification. Néanmoins, pour atteindre effectivement les performances visées lors de la conception ainsi que les objectifs ambitieux en matière de réduction des émissions de GES fixées par la Suisse et l'UE, il est important d'impliquer les occupants du bâtiment, afin de les informer et d'influencer leur comportement si nécessaire et dans la mesure du possible (réglage du confort thermique, éclairage, équipements, mobilité).
THE4BEES se concentre sur les changements de comportement des utilisateurs nécessaires pour parvenir à une réduction de la consommation d'énergie et des émissions de GES. Ces modifications seront rendues possibles par l'utilisation d'applications TIC innovantes développées par l'écosystème d'innovation mis en place par le projet.
Le projet va créer une forme de laboratoire transnational impliquant les milieux universitaires, les décideurs et les administrations clés, les PME régionales et les occupants des bâtiments. L'objectif est d'effectuer une co-création d'applications logicielles innovantes dédiées aux occupants des bâtiments (applications mobiles, serious game, interaction sociale).
Ces applications seront utilisées par les groupes cibles dans les sites de démonstration (écoles, habitats, bureaux) afin d'encourager les changements de comportement en matière d'efficacité énergétique et de réduction de l'empreinte carbone. L'impact des outils développés sera mesuré et évalué. Ces données seront précieuses pour orienter les politiques publiques dans ce domaine. L'exploitation durable des outils sera également analysée afin d'en maximiser l'efficacité et de les valoriser au mieux sur le plan économique.
Ce projet est cofinancé par l'Union Européenne au travers du programme arc alpin (priorité low-carbon alpine space).
La partie suisse du projet est cofinancé par l'ARE et le canton de Fribourg.

Project Lead
Jean-Pierre Bacher
Duration
Start Date: 16/12/2015
End Date: 15/12/2018
Type of Financing
Office fédéral du développement territorial ARE
Fribourg Development Agency
HEIA-FR
Funding (Euro)
Total eligible costs 2'694'646
ERDF Grant 2'290'449
Interreg B - Cradle-ALP
Cradle to cradle, circular design and circular substitutions for linear products in industrial manufacturing processes in the Alpine Space

Cradle-ALP aims for mainstreaming cradle to cradle (C2C) approaches, circular design and circular substitutions (from the alpine region) for linear products in industrial processes, in the chemistry /plastics and wood/forestry sectors.
The Alpine Space has many natural resources and the technologies to substitute fossil raw materials and toxic substances from production with circular and environmentally friendly alternatives. This should lead to the fact that materials and products can be led back into a healthy cycle after use. The focus of this project shall be on the substitution of chemical and fossil based/unsustainable materials with more circular, sustainable and bio-degradable ones.
First, the partners will build a broad awareness and understanding in the public, the relevant industries as well as among stakeholders from policy and innovation intermediaries, for the opportunities, barriers and mechanisms of the transformation of industrial products towards higher circularity by means of C2C approaches, circular design and circular substitutions. Business support providers shall be trained to accompany the transformation of businesses along more circular value chains. In a second step, the partners will explore in details and test opportunities for implementing C2C approaches, circular design and circular substitutions along specific value chains in the chemistry /plastics and wood/forestry sectors supported by digital technologies. Building on a thorough multidimensional (technology, policy, economy, etc.) road mapping exercise, transnational groupings of stakeholders ' including businesses ' will be installed, with the aim to transfer the C2C roadmaps into industrial practice along exemplary value chains. Finally, the partners will work towards ensuring a transnational policy convergence towards transnational S4 strategies in the four priority sectors of the project and initiate common crossborder funding instruments for the industrial C2C transformation.
Project Lead
Duration
Start Date: 11.2022
End Date: 10.2025
Financing type
HEIA-FR
Federal Office of territorial development ARE
Fribourg Development Agency
Funding Euro
Total eligible costs 1.953.970
ERDF Grant 1.405.478
Interreg B - INNOBIOVC
Innovation Express for Circular Bioeconomy Value Chains

Providing food, textiles, and energy among others, bioeconomy is a key aspect of our lives. Since the circular bioeconomy sector is still developing, building international circular bioeconomy value chains could become a determining success factor. Establishing such transnational circular bioeconomy value chains is often problematic, as, due to their cross-regional nature, the smaller companies serving a local market do not know each other.
There is a lack of awareness of funding within the Alpine region and the measurement of the impact of regional or entrepreneurial investments into the circular bioeconomy value chain. INNOBIOVC will build on solutions developed by the two Interreg Alpine Space projects ARDIA-NET and AlpLinkBioEco. Based upon the outputs of these projects, INNOBIOVC will create a new tool that allows partners to find out about funding opportunities, best partners, and to measure sustainability gains of circular products. That way the project will help companies to jointly develop new circular products.
Project Lead
Duration
Start Date: 04.2023
End Date: 09.2024
Type of financing
HEIA-FR
Federal Office of spacial development ARE
Funding Euro
Total eligible costs 548.175
ERDF Grant 390.506
Macro-regional Strategy for the Alpine Region
TRANSALP
Accroître le potentiel économique des secteurs stratégiques
Les régions et pays alpins sont confrontés à des défis similaires, qu'il s'agisse de la promotion économique, du changement climatique ou des questions d'énergie ou de transports. La Stratégie macro-régionale pour la région alpine (EUSALP) a été élaborée pour soutenir la coopération transfrontalière existante et renforcer durablement l'Espace alpin. La Conférence de lancement d'EUSALP a eu lieu les 25 et 26 janvier 2016 à Brno, en Slovénie. Sept pays - dont la Suisse - et quarante-huit régions participent à la Stratégie. Les régions - en Suisse les cantons - jouent un rôle déterminant dans ce processus.
En Suisse, Innosquare Clusters a été choisi pour la représenter au sein du groupe de travail 2 "Accroitre le potentiel économique des secteurs stratégiques".

Project Lead
Michael Keller
Start Date
February 2016
End Date
December 2019
Type of Financing
HEIA-FR
Office fédéral du développement territorial ARE